Running is as easy as 1-2-3
There are two kinds of runners in the world; those who love it and those who don’t. I am definitely the latter of the group. However, the one thing they all have in common is, you guessed it, running. Regardless of whether you are enjoying your time on your run or not, we all know that it is the best way to impact our health goals of staying in shape, losing weight, relieving stress or whatever it is why we feel the need to run. What if I told you that all you need to know are three simple things?
 Running certainly has its benefits, we all know this. The problem arises when injuries creep up on us while doing the one thing we know is intended to keep us healthy. You can choose not to run. That would eliminate your chances all together of getting injured from running, guaranteed, or you can take these three simple tips to heart and implement them on your next run. Granted these will take some practice and patience, but when observed routinely, your risk of injury is certain to diminish, making your opinion on running more personal than physical.
Running certainly has its benefits, we all know this. The problem arises when injuries creep up on us while doing the one thing we know is intended to keep us healthy. You can choose not to run. That would eliminate your chances all together of getting injured from running, guaranteed, or you can take these three simple tips to heart and implement them on your next run. Granted these will take some practice and patience, but when observed routinely, your risk of injury is certain to diminish, making your opinion on running more personal than physical.
Tip #1: Know Your Cadence
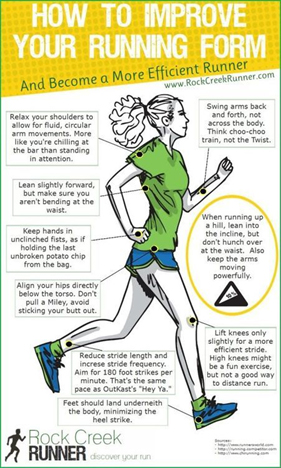
Cadence is the number of steps you take per minute. The common number for optimal cadence is 180 steps per minute, but if you are trying to run at an easy comfortable pace, you should be running at least 170 steps per minute. By staying in this range, you will reduce the impact forces on your legs, cut your injury risk, and even improve your running efficiency. How? With a shorter, faster stride, you’re “bounding” less and not introducing the stress that accompanies longer, more impactful strides. In other words, you’ll get hurt less often and probably get faster (Yah!).
Tip #2: Proper Foot Strike
Before you rush out to by that super cool pair of running shoes that will help you to run faster, jump higher, and solve world hunger, you must first understand that contrary to what Mars Blackmon tells us, “It’s not about the shoes”. It is more about where your foot strikes the ground. Many of us start out to fast, placing our foot out in front when we are striking the ground, this will both increase the level of impact on the body and slow your momentum down with each step. Your foot should strike the ground directly under your hips, propelling you forward. Changing your foot strike, although a bit awkward at first, will reduce the impact on your legs and cut your injury risk by creating a more fluid and efficient stride.
Tip #3: Run Tall and Proud
Remember all those times your mom used to tell you to stand up straight? Well, she has now officially become your running coach. Too many of us feel the need to “lean in” when we are running, but that is not a recommended strategy when trying to be most efficient in our running. We all want to have a forward lean, but that should not be happening at the waist, but rather at the ankles, where it will naturally occur. To help keep you honest, try to imagine that you have a string coming out of the top of your head and some giant puppet master is holding you erect. Too much forward lean will create and energy depletion, causing your body to work harder than it is already being asked.
I hope these tips will provide you with some reprieve from the onset of injury when running. Certainly, there are a variety of factors we must consider beyond just these simple ones, but remembering the fundamentals is the most effective way of evolving with anything we are trying to improve upon.
Ready to #feelbetter?
You're just a click away from a wicked good massage!
-

60 Minute Massage Gift Card
$170.00 Add to cart -

90 Minute Massage Gift Card
$255.00 Add to cart -

Mini Aer Small Room Air Purifier
$149.00 Add to cart -
Sale!

Thera-Pearl Sports Pack/Hot Cold
Original price was: $14.99.$12.99Current price is: $12.99. Add to cart -

3 Somadome Sessions Gift Card
$135.00 Add to cart -

20 Minute Somadome Gift Card
$45.00 Add to cart -
Sale!

TheraBand® Stretch Strap
Original price was: $19.99.$14.99Current price is: $14.99. Add to cart -

TheraBand CLX Connective Loop
$14.99 Select options
Muscle Strains
A strain, sometimes referred to as a pulled muscle, is a muscle injury produced by excessive tensile stress that causes fibers to tear within the tissue. A muscle strain does not usually result from excess stretch alone, but from a combination of tension and contraction. Muscle strains can develop when excess tension is placed on…
Read MoreShin Splints or Compartment Syndrome?
One of the most common overuse injuries affecting the lower extremity is the condition known as shin splints. While the term shin splints routinely is used, especially among the athletic population, it does not represent a specific clinical pathology. Instead, it describes chronic shin pain resulting from overuse. It occurs in two regions of the…
Read MoreAn Alternative Approach to Stretching
Clinicians, athletes and rehabilitation specialists advocate stretching as a means for injury prevention and treatment. The primary purpose of any stretching technique is to enhance pliability and flexibility in the soft tissues. It is also routinely incorporated with massage in the treatment of pain and injury conditions. There are many different stretching techniques, which all…
Read MoreGanglion Cysts
The highly refined palpation skills of massage practitioners are such that we often identify tissue abnormalities before the client is aware of them. An indication that we should refer a patient for further evaluation is when we identify something we aren’t sure of but know shouldn’t normally be there. One such example may occur with…
Read MoreWhat Is the “End Feel”?
Some of the most valuable assessment information is derived from relatively simple procedures such as passive range-of-motion tests. While many massage practitioners have been exposed to the fundamental concepts of active and passive range-of-motion testing, most have not learned how to use this information effectively in a clinical environment. In this article, we will focus…
Read MoreHow Accurate Is That Test?
Physical assessment is considered one of the most accurate ways to assess function of the locomotor tissues of the body. While we can often gain valuable information about structural problems through high-tech diagnostic procedures like X-ray or MRI, these procedures tell us very little about the function of the tissues involved in creating and limiting…
Read MoreWhen Is It Tendinitis?
Tendinitis is one of the most common diagnoses for soft tissue pain resulting from repetitive motion. As repetitive motion disorders have dramatically increased, so has the incidence of tendinitis. However, recent investigations into the cellular nature of tendon pathologies have brought forth interesting discoveries that may alter the way tendinitis is treated. In this month’s…
Read More- « Previous
- 1
- …
- 18
- 19
- 20

